Quantum Random Walk
The behavior of quantum random walks (QRWs) using the Creutz ladder model
Overview
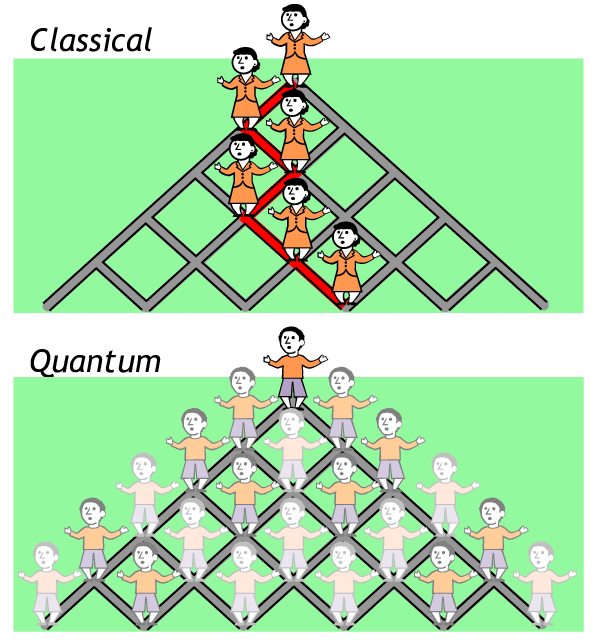
In this project, we explored the behavior of quantum random walks (QRWs) using the Creutz ladder model, a quantum lattice structure known for its localization properties. Our focus was on examining how quantum particles behave within this confined system and comparing it to classical random walks (CRWs).
Key Contributions
- Classical and Quantum Walk Regimes: We validated the expected diffusive behavior in CRWs and the ballistic regime in QRWs. These foundational insights highlight the differences between classical and quantum behavior in random walks.
- Localization in the Creutz Ladder Model: By introducing randomness through the Grover coin operator and applying combinatorial methods, we demonstrated that the quantum particle’s movement is confined within a specific region. This result enhances our understanding of how structured lattices impact quantum behavior.
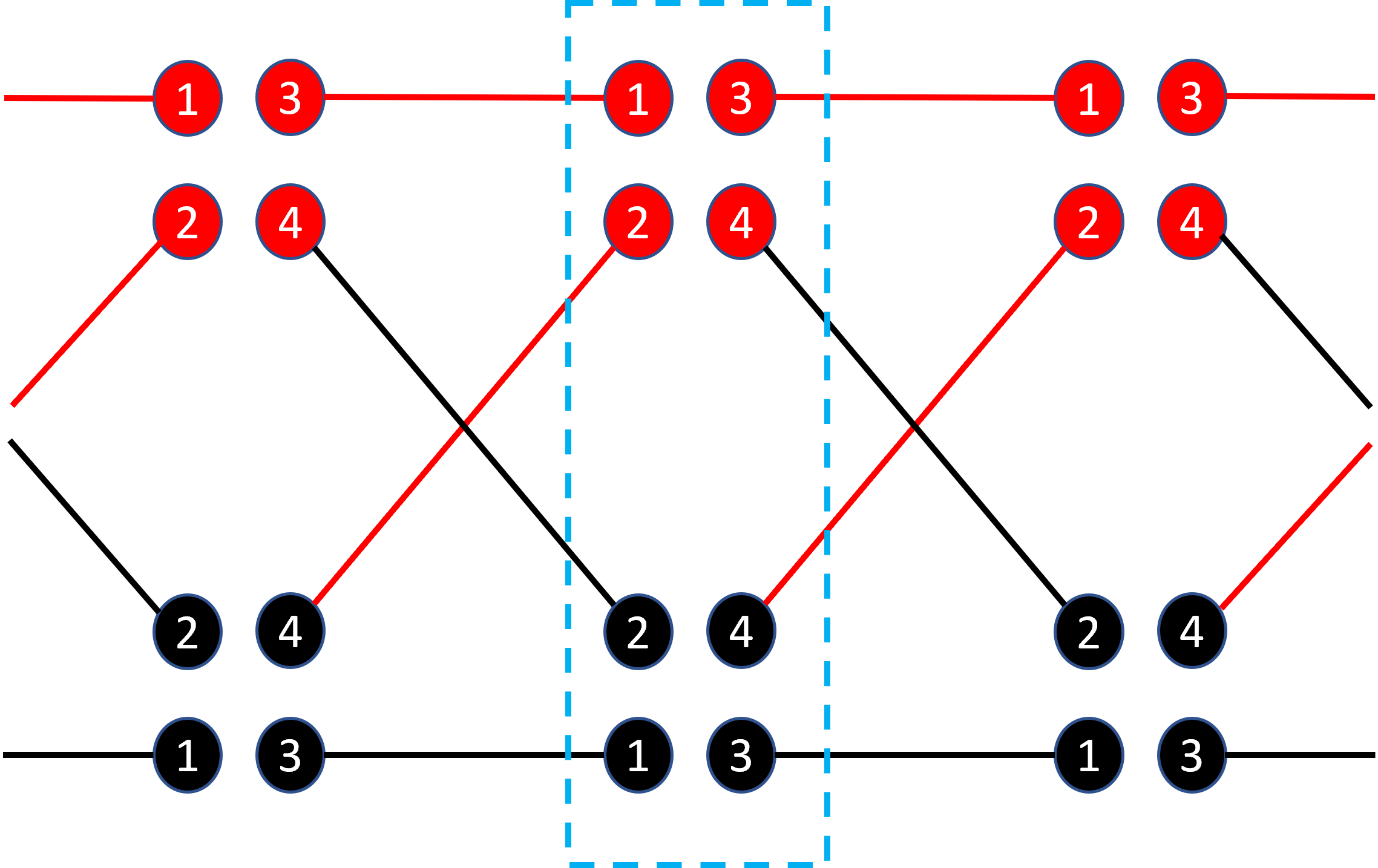
- Numerical Simulations: We conducted numerical simulations that supported our analytical results, showing that the probability of the particle moving beyond a confined range is zero. This confirmation strengthens our findings and demonstrates the effectiveness of our methods.
Visualization
We visualized the quantum walk on the Creutz ladder, numerically verifying that the particle remains within a confined region. Additionally, we observed recurring patterns in the particle’s location probability over time, which opens up new avenues for further research.
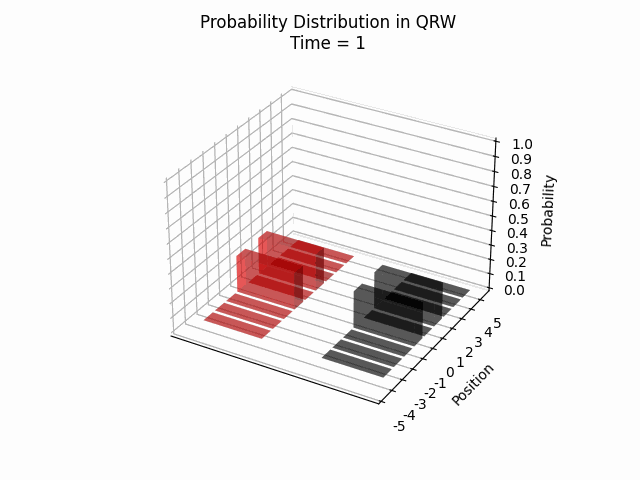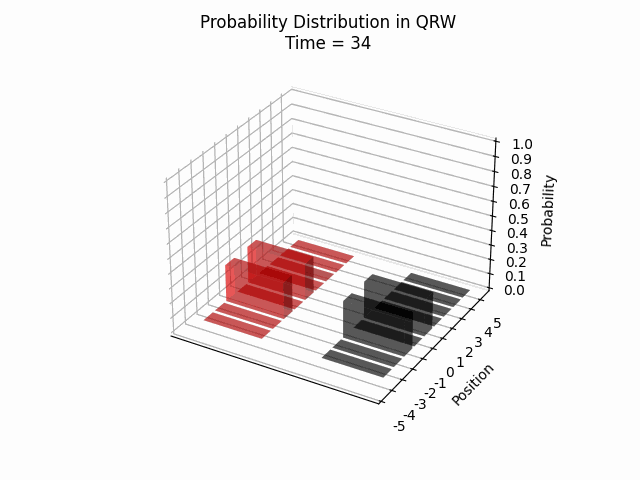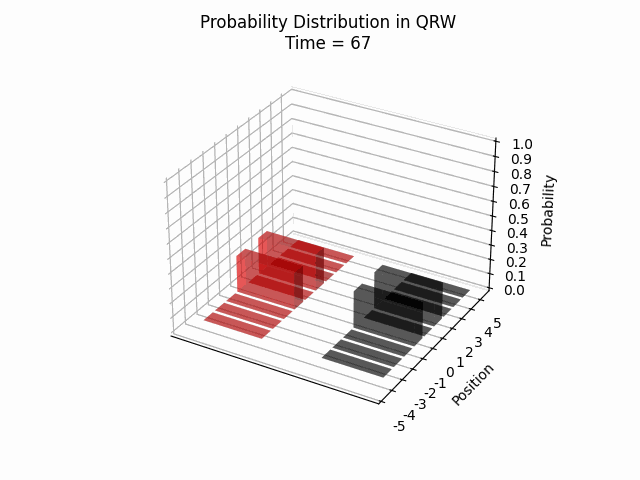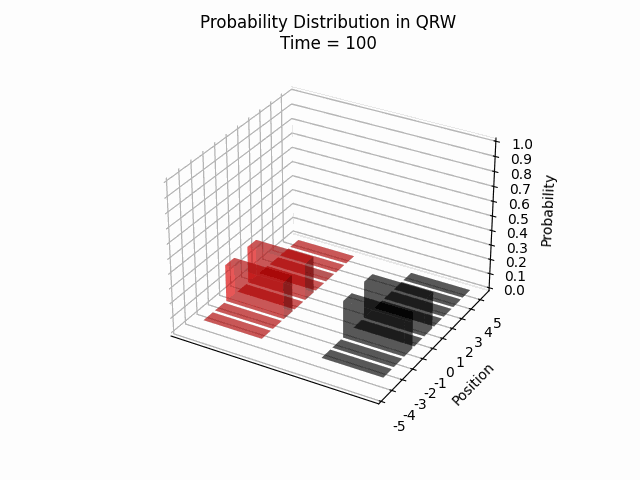
Conclusion
These findings contribute significantly to our comprehension of QRWs and their potential applications. The demonstrated confinement of quantum walks within the Creutz ladder model suggests promising avenues for future research into controlled quantum systems and their practical implementations.
Future Directions
-
Exploration of Alternative Lattice Models: Investigate different lattice structures to understand how they affect QRW behavior and localization.
-
Development of Quantum Algorithms: Utilize the confinement properties observed in this study to design quantum algorithms that require controlled particle movements.
-
Experimental Validation: Conduct real-world experiments to verify the theoretical and numerical results of this study.
Learn More
For a deeper dive into our work, including detailed equations, proofs, and data, refer to our full report.
This project was a collaborative effort under the guidance of our mentors and head mentors. The findings represent a preliminary study in the field of quantum random walks, with opportunities for further exploration and learning.